The second law of thermodynamics states that all natural processes displace towards their minimum energy state (equilibrium). This state, in turn, relates to a maximum disorder condition, which means "CHAOS".
However, fulfilling this thermodynamic law, our universe has found the way to build "The Cosmos", that impressive structure made up of galaxies, stars and planets, whose etymological definition means precisely "ORDER".
Human enterprises must also be formed, structured, designed, following an established order. The achievement of good results requires a significant energy consumption, which for human processes and attitudes means "DISCIPLINE".
Business Engineering structures, designs, controls, plans, all organizational activities from their basic processes. This implies visualizing and handling business matters from a "systemic" frame of reference, where all components (starting from their human elements) are strictly interrelated.

Founded on very similar principles, Business Engineering is highly compatible with all quality systems, in particular with ISO standards.
Business Engineering designs those processes to be controlled by quality systems, builds specific procedures for each organization, based on the operating reality of the company, so the planned results can be attained. Moreover, it leads to an effective and efficient operation control, by applying its own measurement, analysis and improvement techniques.
PROCESS BASED APPROACH
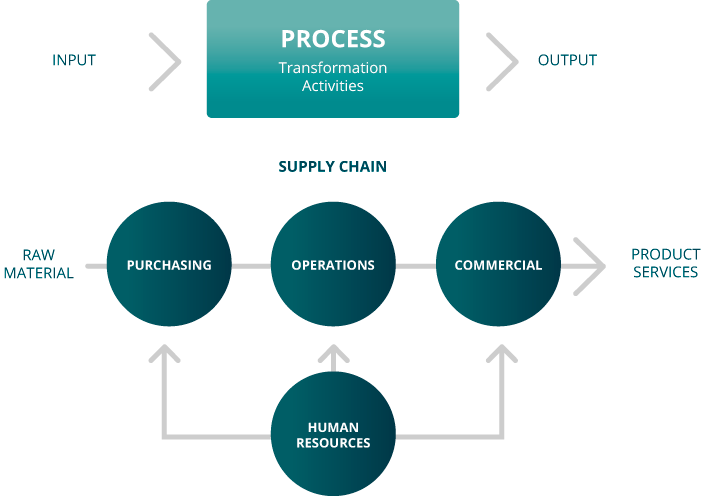
For instance, a top management Business Engineering, based on ISO 9001:2008, shall be oriented to designing tools and solutions on the following aspects:
Quality management principles.
- Control concepts.
- Process based approach.
- PEVA methodology.
- Customer satisfaction.
- QMS benefits.
QMS general requirements.
- Organizational processes.
- Outsourced processes control.
- Documentation requirements.
- Management procedures.
- Operating procedures.
- Documents control.
- Records control.
Management responsibility.
- Management commitment.
- Customer focus.
- QMS planning.
- Responsibility and authority.
- Management representative.
- Internal communication.
- Management review.
- Resources provision.
- Human resources.
- Planning of product realization.
- Design and development.
- Purchasing.
- Production and service provision.
- Infrastructure/Work environment.
Measurement, analysis and improvement.
- Customer satisfaction.
- Internal audit.
- Processes monitoring and measurement.
- Product monitoring and measurement.
- Non conforming product control.
- Data analysis.
- Continual improvement.
- Corrective action.
- Preventive action.